What Process Can Prevent These Errors From Occurring
What is Fault Proofing?
Quality Glossary Definition: Mistake proofing
Likewise called: poka-yoke, neglect-safing
Mistake proofing, or its Japanese equivalent poka-yoke (pronounced PO-ka yo-KAY), is the use of any automatic device or method that either makes it impossible for an error to occur or makes the error immediately obvious once it has occurred. It is a common procedure analysis tool.
When to Use Error Proofing
- When a process step has been identified where man mistake tin can cause mistakes or defects to occur, especially in processes that rely on the worker'southward attention, skill, or experience
- In a service process, where the customer can make an fault which affects the output
- At a hand-off step in a process, when output (or for service processes, the client) is transferred to another worker
- When a minor error early on in the process causes major bug later in the procedure
- When the consequences of an error are expensive or dangerous
Error Proofing Procedure
- Obtain or create a flowchart of the process. Review each step, thinking about where and when human errors are probable to occur.
- For each potential error, work back through the process to find its source.
- For each error, think of potential ways to get in impossible for the fault to occur. Consider:
- Emptying: eliminating the pace that causes the error.
- Replacement: replacing the step with an fault-proof one.
- Facilitation: making the right action far easier than the error.
- If y'all cannot make it impossible for the error to occur, recall of ways to detect the error and minimize its effects. Consider inspection methods, setting functions, and regulatory functions expanded on beneath.
- Choose the best error-proofing method or device for each error. Test it, and so implement it. Three kinds ofinspection methods provide rapid feedback:
- Successive inspection is done at the next pace of the process past the side by side worker.
- Cocky-inspection means workers check their own work immediately subsequently doing information technology.
- Source inspection checks, earlier the process step takes place, that weather are right. Often it'due south automatic and keeps the process from proceeding until conditions are correct.
Setting and Regulatory Functions
Setting functions are the methods by which a process parameter or product aspect is inspected for errors:
- The contact or concrete method checks a concrete characteristic such every bit diameter or temperature, frequently using a sensor.
- The motion-step or sequencing method checks the procedure sequence to brand sure steps are done in club.
- The fixed-value or grouping and counting method counts repetitions or parts, or it weighs an item to ensure abyss.
- A fourth setting function is sometimes added, data enhancement, which makes sure data is bachelor and perceivable when and where required.
Regulatory functions are signals that alarm the workers that an mistake has occurred:
- Warning functions are bells, buzzers, lights, and other sensory signals. Consider using colour-coding, shapes, symbols, and distinctive sounds.
- Control functions prevent the process from proceeding until the fault is corrected (if the error has already taken identify) or conditions are correct (if the inspection was a source inspection and the error has not yet occurred).
Error Proofing Case
The Parisian Feel eating house wished to ensure loftier service quality through error proofing. They reviewed the deployment chart (a detailed flowchart that shows who performs each step) of the seating process shown below and identified human errors on the part of restaurant staff or customers that could cause service problems.
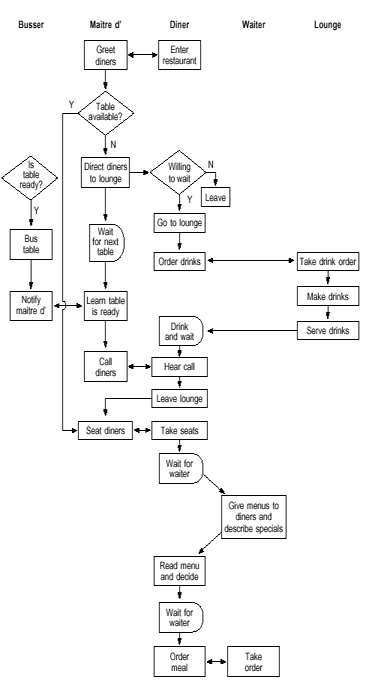
Error Proofing: Restaurant's deployment chart
The first potential error occurs when customers enter. The maitre d' might not notice a customer is waiting if the maitre d' is escorting other customers to their table, checking on table condition, or conferring with kitchen staff.
The mistake proofing device is an electronic sensor on the entrance door. The sensor sends a signal to a vibrating pager on the maitre d's belt to ensure that the maitre d' always knows when someone enters or leaves the restaurant. Other mistake proofing methods replaced the procedure steps requiring the maitre d' to leave the front door to seat customers.
A possible error on the customers' office was identified at the pace when diners are called from the lounge when their table is ready. They might miss the telephone call if the lounge is noisy, if they are engrossed in conversation, or if they are hard of hearing.
The mistake proofing chosen by the team was to replace the pace of the procedure in which the maitre d' called the customer's name over the loudspeaker. Instead, during the greeting step, the maitre d' notes a unique visual identifier of one or more members of the party. When the table is ready, the table busser notifies the waiter, who comes to the maitre d' and learns how to identify the customers. The waiter finds the customers in the lounge, escorts them to their table, gives them menus, and takes additional potable orders.
Not only does this fault proofing method eliminate a customer-caused problem, information technology improves the restaurant ambiance past eliminating the abrasive loudspeaker, keeps the maitre d' at the front end door to greet customers, creates a sense of exceptional service when the waiter "magically" knows the customers, and eliminates additional waiting fourth dimension at the mitt-off betwixt maitre d' and waiter.
Adapted from The Quality Toolbox, Second Edition, ASQ Quality Press.
rodrigueztwentone.blogspot.com
Source: https://asq.org/quality-resources/mistake-proofing
0 Response to "What Process Can Prevent These Errors From Occurring"
Post a Comment